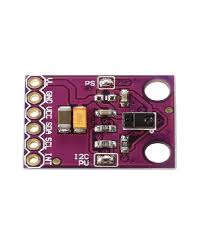
MCU-219 INA219 I2C Bi-directional Current / Power Monitoring Sensor Module COM51
The MCU-219 (INA219) is a precision, bidirectional, I2C-based current, voltage, and power monitoring sensor module. It is often used in embedded systems and IoT projects to measure the power consumption of devices.
Key Features:
- Voltage Measurement: Measures voltage directly from the device under test.
- Current Measurement: Measures current using a shunt resistor.
- Power Measurement: Calculates power based on the measured voltage and current.
- Bi-Directional Capability: Can measure current in both directions, useful for charging/discharging applications.
- I2C Communication: Interfaces with microcontrollers like Arduino, ESP32, or Raspberry Pi over I2C.
- High Accuracy: Provides 12-bit resolution for voltage and current measurements.
Specifications:
- Operating Voltage: 3.0V to 5.5V (logic level compatible with most microcontrollers).
- Current Range: Typically up to ±3.2A (depends on the shunt resistor used).
- Voltage Range: 0V to 26V (maximum bus voltage).
- Resolution: 12-bit ADC resolution for both voltage and current.
- I2C Address: Default 0x40 (can be changed to one of four addresses).
- Shunt Resistor: Typically 0.1Ω (may vary depending on the module).
Pinout:
- VCC: Power supply (3.3V or 5V).
- GND: Ground.
- SCL: I2C Clock.
- SDA: I2C Data.
How It Works:
- The INA219 measures the voltage drop across a precision shunt resistor connected in series with the load.
- Using Ohm’s law (V=IRV = IRV=IR), it calculates the current through the load.
- It then calculates the power (P=IVP = IVP=IV) being consumed by the load.
- The measurements are accessed via the I2C interface.
Applications:
- Power monitoring for battery-powered devices.
- Solar power systems.
- DC motor control.
- Energy management in IoT projects.
Getting Started (Example with Arduino):
- Connect the module to your microcontroller:
- VCC → 3.3V/5V
- GND → GND
- SCL → I2C Clock
- SDA → I2C Data
- Install the Adafruit INA219 library in the Arduino IDE.
Use the following sample code:#include#include Adafruit_INA219 ina219; void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); if (!ina219.begin()) { Serial.println("Failed to find INA219 chip"); while (1) { delay(10); } } Serial.println("INA219 Initialized."); } void loop() { float shuntvoltage = ina219.getShuntVoltage_mV(); float busvoltage = ina219.getBusVoltage_V(); float current_mA = ina219.getCurrent_mA(); float power_mW = ina219.getPower_mW(); Serial.print("Bus Voltage: "); Serial.print(busvoltage); Serial.println(" V"); Serial.print("Shunt Voltage: "); Serial.print(shuntvoltage); Serial.println(" mV"); Serial.print("Current: "); Serial.print(current_mA); Serial.println(" mA"); Serial.print("Power: "); Serial.print(power_mW); Serial.println(" mW"); Serial.println(""); delay(1000);
Frw 4,500























.jpeg)